A trade mall design can be done through numerous analysis and research. However, there is one very important matter in the study, which is business thinking.
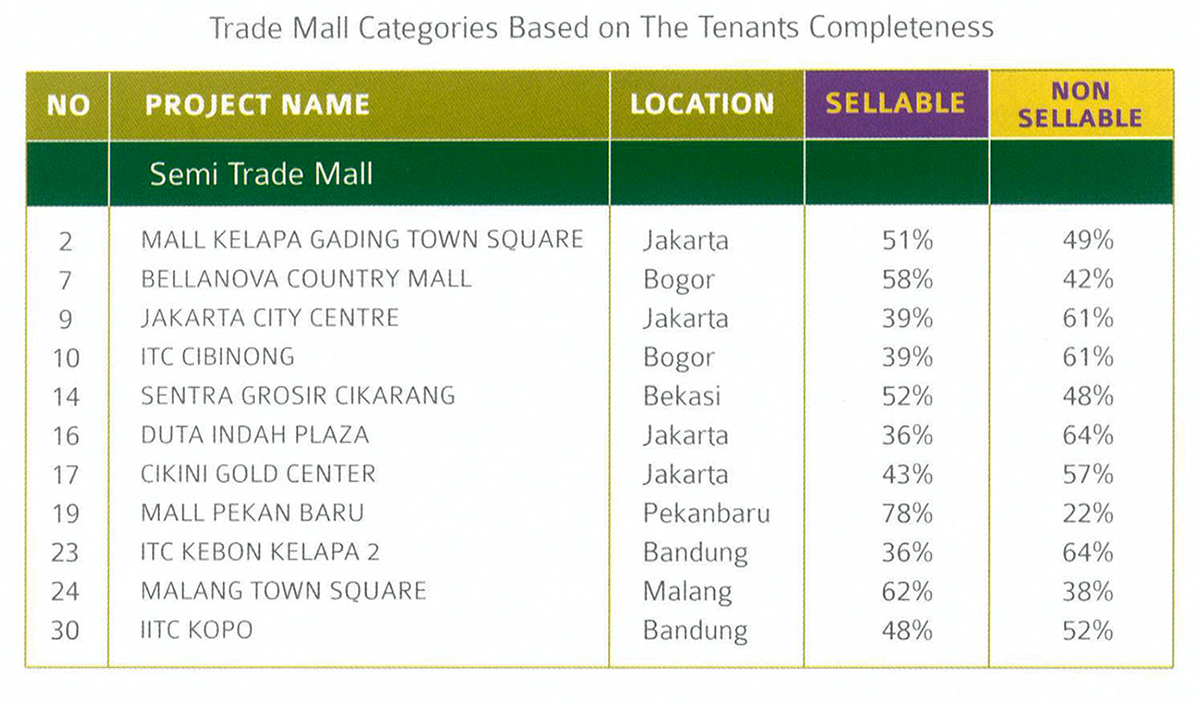
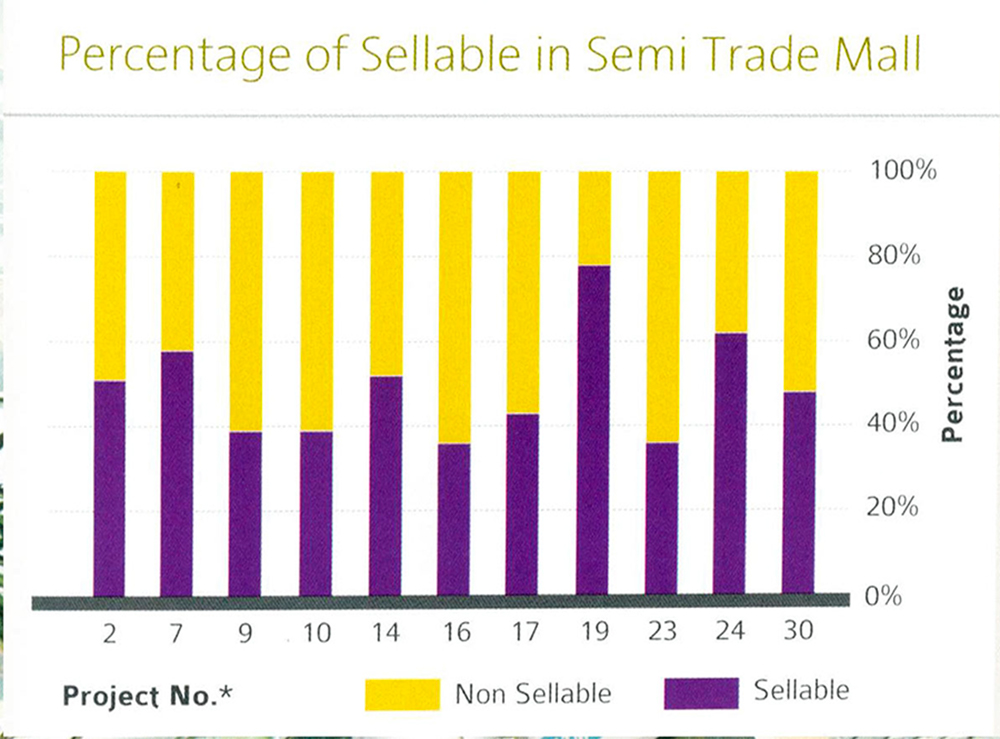
Public analysis based on business way of thinking will produce a marketable and profitable design. From various trade malls nowadays, we can categorize them into some big categories based on the completeness of the tenants, among others:
- Anchor tenant, is a large leased shopping area. Anchor tenants consist of 6 main functions, which are: supermarket, department store, game center, bookstore, food court, and cinema.
- Big tenant is also leased, although not as large as the anchor tenant, but it is bigger than small shops. Usually big tenants function as restaurants, etc.
- Small tenant/shop, is usually a shop unit that is strata title in nature. The items sold in them are varied, such as clothes, food, electronic appliances, etc.
These tenants are important in determining a category, because their existence is a factor to attract visitors. The more complete tenant existence in a trade mall, the further it can reach the surrounding communities. This is because the larger the tenant, more various items are available to trade, this will increase the selling factor of this tenant to its surrounding communities (for instance: department stores and supermarkets).
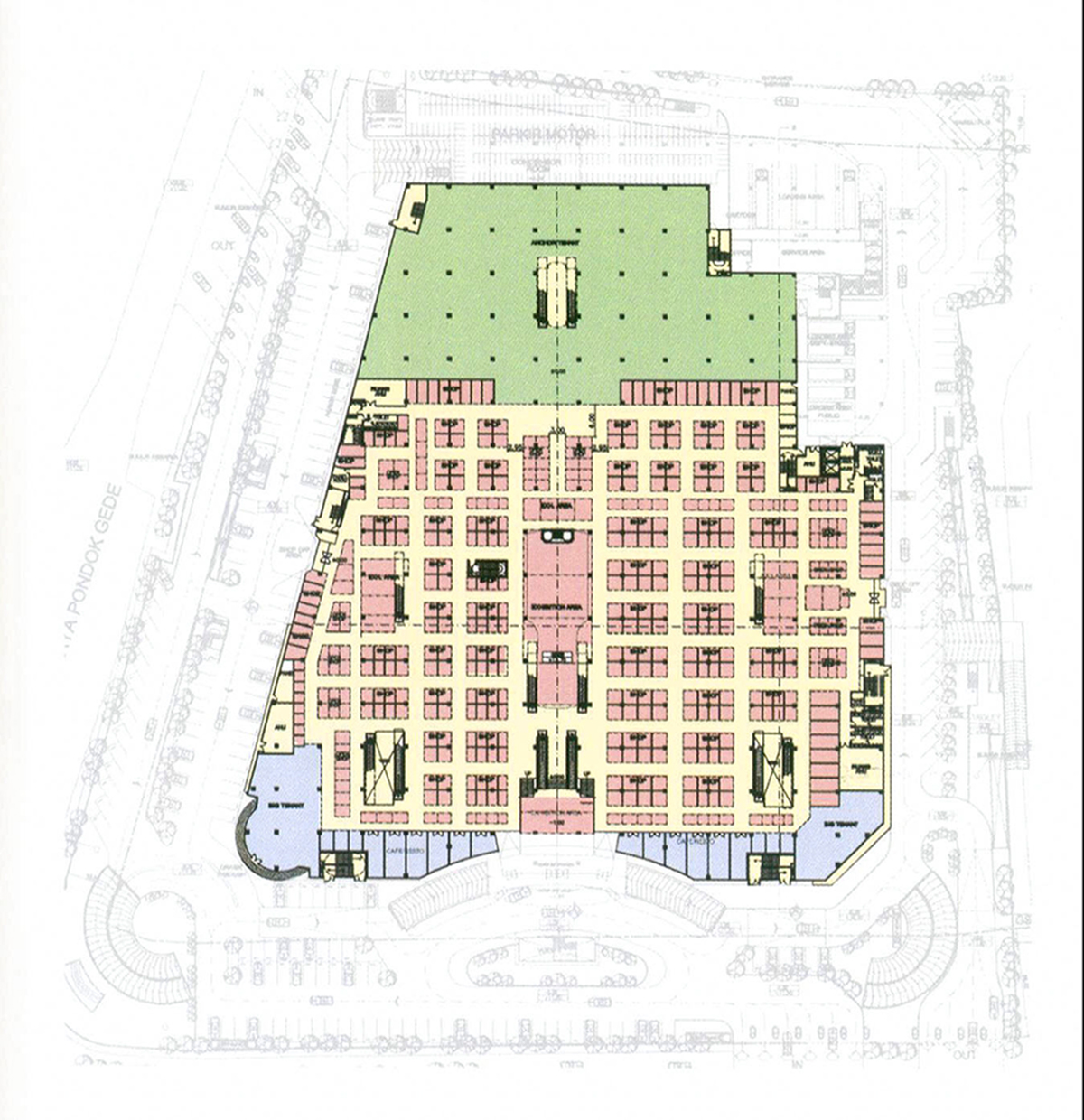
In a macro point of view, a trade mall equipped with a complete anchor tenant, will be able to attract the public to come in a larger scope, and vice versa. In a micro point of view, if an anchor tenant which acts as a big magnet is placed in the right position, will become an effective center of interest to the sellers and shop owners. This effectiveness is formed when visitors walk to the anchor tenant and at the same time passing other small shops. This shows that positions and the amount of anchor tenants can affect the flow of visitors movements, and create a pattern which will determine profitable shop placements.
Anchor tenants are generally placed on the sides of a trade mall. Placement of one anchor tenant to another is the most profitable positioning for shops, because it creates a great flow of visitors movement, These profitable points and locations can be maximized by adjusting the size width of the anchor tenants, entrance positions, etc. With the right design strategy, a significant increase of visitor movements flow inside the trade mall will be created.
Other than anchor tenants, another type of leased tenant is a big tenant. Big tenant or more commonly known as mini anchor is a form of anchor in a smaller scale, but with the same function which is to attract visitors movement flow. Big tenants generally function as food and beverages such as restaurants, fast foods, cafe, outdoor cafe, other big shops for electronic appliances, cellphones, computers, furniture, boutique, also a few ATM centers and some banks branch offices. The placement is different from that of an anchor tenant. Big tenants are not placed independently, but rather grouped with other big tenants.
“The more complete tenant existence in a trade mall, the further it can reach the surrounding communities. This is because the larger the tenant, the more various items are available to trade.”
While anchor tenants affect the movement flow in the main channel, which is generally located at the center of the trade mall, big tenants are focusing to attract visitors to side parts of the trade mall. The objective is for the side parts of the mall to have their own magnet to attract visitors to the shops located in those areas.
Small tenants/shops are the tenants with the smallest size and area, and the status is strata title/for sale. Although small in size, shops are the main fund source for the developers to finance the development of a trade mall. Therefore, shops are the main enablers of cash flow. Their positions and amounts must be calculated and strategized carefully. Small tenant/ shops are divided into 3 categories: close, open and casual leasing.
Close is usually known as shops, separated with other shops by massive walls from floor to ceiling, giving a sense of closeness, and usually only have 1 or 2 sides for the entrance. The placement of these shops is usually on the sides or center of the building. Usually the ones in the sides are slightly larger than the ones located in the center of the building.
The second category, open, is widely known as kiosk, a kind of shop with semi-permanent walls of 1.5-2 meters. Generally, on the top side of the wall, a display of the items sold is placed. Kiosks have smaller size and cost relatively cheaper than a shop. Kiosks are often placed in the center of the building, with 2-4 sides of the shop exposed to the visitors.
The last small tenant is casual leasing. This type of shop is to be found alongside corridors or atriums of the building. With semi-permanent separators, the casual leasing shop is portable in nature. This is because of the non permanent nature of the shops, which only exist in exhibitions, or only for a period of time. The items sold are usually ‘fixed’ items such as accessories, or ‘seasonal’ such as batik exhibitions, pets, etc.

“In designing a Trade Mall, we need to determine which category we wish for. At this point, the role of business thinking is really reliable because each category of Trade Mall will yield different implications/effect.”

Based on the completeness and the existence of tenants, the trade mall is categorized into 3. The first category is a complete trade mall. In this type of trade mall,all the 3 types of tenants exist: anchor tenant, big tenant and small tenant/ shops. Based on the effectiveness of an anchor tenant, a complete trade mall at least has 4 to 6 anchor tenant functions. This is aimed for a more effective flow
of movements in the trade mall, and will cause the trade mall to be more ‘lively’ and profitable for the shop owners.
The second category is a semi-complete trade mall, where it has a combination of tenants, but not as complete as the complete trade mall. A semi complete trade mall only has 2 or 3 anchor tenants, with some big tenants and shops.
The third category, is trade mall without anchor tenant/trade center, with only combining some big tenants and shops. This category usually has smaller scope or target compared to the other two.
This category usually has smaller scope or target compared to the other two. In designing a trade mall, we need to determine which category we wish for. At this point, the role of business thinking is really reliable, because each category of trade mall will yield different implications/effects. To know what implications to be expected, first we need to determine expected catchment area (scope area), capacity and the extent of the project to be designed. Catchment area is determined by project locations as well as the market conditions and potential. All designs and analysis will determine the category of trade mall to design, and how big is the appeal to the surrounding communities.


